missing translation for 'onlineSavingsMsg'
Learn More
Learn More
Descripción
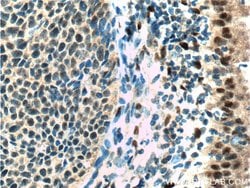
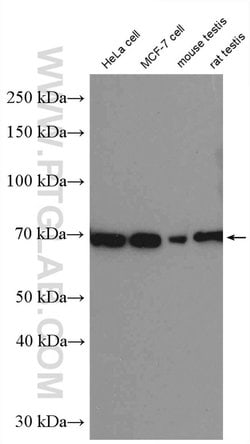
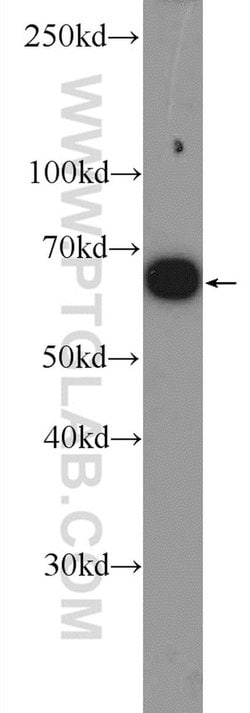
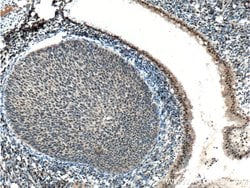
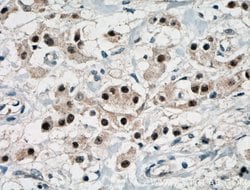
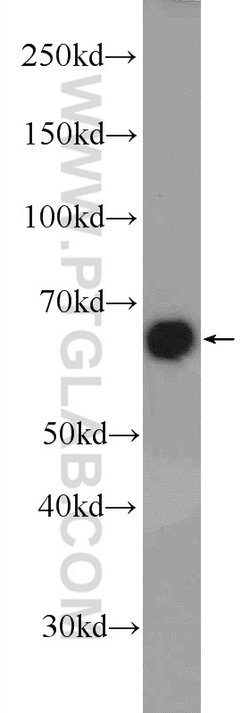
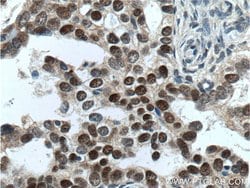
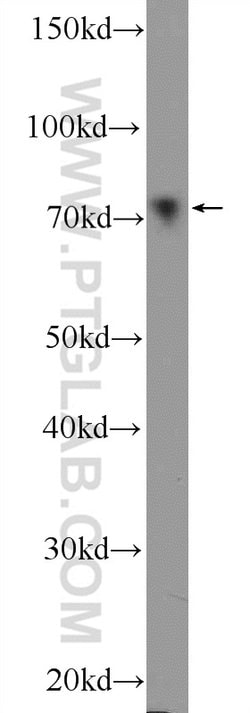
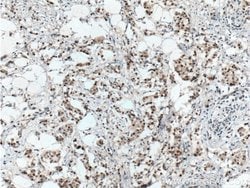
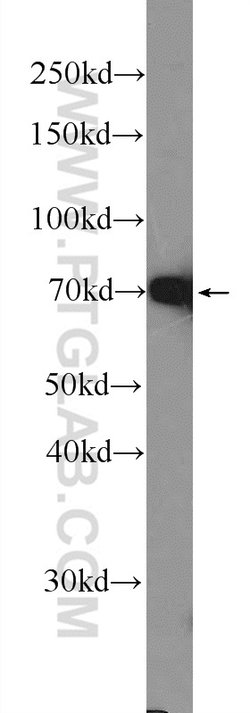
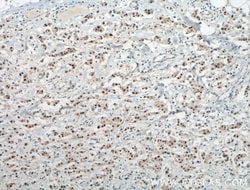
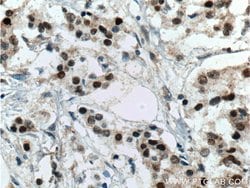
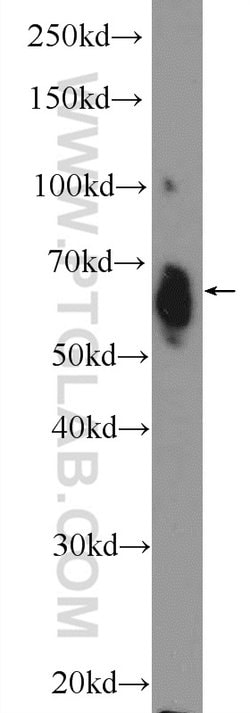
Estrogen Receptors (ER) are members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily of nuclear receptors. The estrogen receptor is a ligand-activated transcription factor, that when bound to estrogen hormone, induces a conformational change that allows dimerization and binding to estrogen response elements (ERE) in DNA. When bound to EREs, ER can positively or negatively regulate gene transcription through the recruitment of coactivator or corepressor proteins. There are two different forms of the estrogen receptor, alpha and beta, encoded by separate genes (ESR1 and ESR2, respectively). Due to alternative RNA splicing, at least 4 estrogen receptor-alpha isoforms are known to exist (Isoform 1 (66 kDa), Isoform 2 (53 kDa), Isoform 3 (47 kDa), Isoform 4 (35 kDa)). Estrogen receptors are widely expressed in different tissue types and are essential for sexual development and reproductive function. They also play a role in other tissues such as bone. Estrogen receptors are involved in pathological processes including breast cancer, endometrial cancer, and osteoporosis.
Especificaciones
Especificaciones
| Antígeno | ER |
| Aplicaciones | Western Blot, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin) |
| Clasificación | Polyclonal |
| Concentración | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Conjugado | Unconjugated |
| Formulación | PBS with 50% glycerol and 0.1% sodium azide; pH 7.3 |
| génica | ESR1 |
| N.º de referencia del gen | P03372, P06211, P19785 |
| Alias de gen | ER, ER alpha, Era, ESR, ESR1, ESRA, Estradiol receptor, Estrogen receptor, estrogen receptor 1, NR3A1 |
| Símbolos de los genes | ESR1 |
| Mostrar más |
Título del producto
By clicking Submit, you acknowledge that you may be contacted by Fisher Scientific in regards to the feedback you have provided in this form. We will not share your information for any other purposes. All contact information provided shall also be maintained in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
Spot an opportunity for improvement?